Most of you are already familiar with the SQL database and have a piece of useful knowledge on either MySQL, Oracle, or other SQL databases. In the last several years, NoSQL database is getting widely adopted to solve various business problems.
It is helpful to understand the difference between SQL and NoSQL database, and some of available NoSQL database that you can play around with.
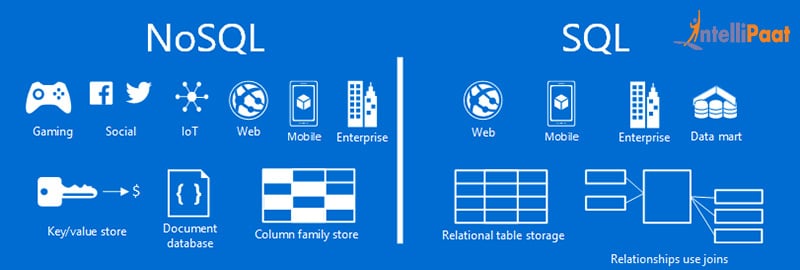
SQL vs. NoSQL: High-Level Differences
SQL databases are essentially called Relational Databases (RDBMS); whereas NoSQL database is primarily called as a non-relational or distributed database.
SQL databases are table based databases whereas NoSQL databases are document based, key-value pairs, graph databases or wide-column stores. This means that SQL databases represent data in the form of tables which consists of n number of rows of data whereas NoSQL databases are the collection of a key-value pair, documents, graph databases or wide-column stores which do not have standard schema definitions which it needs to adhere to.
SQL databases have predefined schema whereas NoSQL databases have the dynamic schema for unstructured data.
SQL databases are vertically scalable whereas the NoSQL databases are horizontally scalable. SQL databases are scaled by increasing the horse-power of the hardware. NoSQL databases are mounted by increasing the databases servers in the pool of resources to reduce the load.
SQL databases use SQL ( structured query language ) for defining and manipulating the data, which is very powerful. In the NoSQL database, queries are focused on the collection of documents. Sometimes it is also called as UnQL (Unstructured Query Language). The syntax of using UnQL varies from database to database.
SQL database examples: MySql, Oracle, SQLite, Postgres, and MS-SQL. NoSQL database examples: MongoDB, BigTable, Redis, RavenDb, Cassandra, Hbase, Neo4j and CouchDB
For complex queries: SQL databases are the good fit for the complex query intensive environment whereas NoSQL databases are not a good fit for complex queries. On a high-level, NoSQL doesn’t have standard interfaces to perform complex queries, and the queries themselves in NoSQL are not as powerful as SQL query language.
For the type of data to be stored: SQL databases are not best fit for hierarchical data storage. But, NoSQL database fits better for the hierarchical data storage as it follows the key-value pair way of storing data similar to JSON data. NoSQL database is highly preferred for the large data set (i.e., for big data). Hbase is an example for this purpose.
For scalability: In most typical situations, SQL databases are vertically scalable. You can manage increasing load by increasing the CPU, RAM, SSD, etc., on a single server. On the other hand, NoSQL databases are horizontally scalable. You can add a few more servers easily in your NoSQL database infrastructure to handle the massive traffic.
For high transactional based application: SQL databases are the best fit for heavy-duty transactional type applications, as it is more stable and promises the atomicity as well as the integrity of the data. While you can use NoSQL for transactions purpose, it is still not comparable and stable enough in high load and for complex transactional applications.
For support: Excellent support is available for all SQL database from their vendors. There are also a lot of independent consultations which can help you with SQL database for a considerable scale deployment. For some NoSQL database, you still have to rely on community support, and only limited outside experts are available for you to set up and deploy your large scale NoSQL deployments.
For properties: SQL databases emphasizes ACID properties ( Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability) whereas the NoSQL database follows the Brewers CAP theorem ( Consistency, Availability, and Partition tolerance )
For DB types: On a high-level, we can classify SQL databases as either open-source or close-sourced from commercial vendors. NoSQL databases can be sorted by way of storing data as graph databases, key-value store databases, document store databases, column store database, and XML databases.
SQL Database Examples
1. MySQL Community Edition
MySQL database is a viral open-source database. It is generally stacked with apache and PHP, although it can also be stacked with nginx and server-side javascripting using Node Js. The following are some of MySQL benefits and strengths:
Replication: By replicating MySQL database across multiple nodes the workload can be reduced massively increasing the scalability and availability of business application
Sharding: MySQL sharding os useful when there is large no of write operations in a high traffic website. By sharding MySQL servers, the app is partitioned into multiple servers dividing the database into small chunks. As low-cost servers can be deployed for this purpose, this is cost effective.
Memcached as a NoSQL API to MySQL: Memcached can be used to increase the performance of the data retrieval operations giving an advantage of NoSQL API to MySQL server.
Maturity: This database has been around for a long time, and tremendous community input and testing has gone into this database making it very stable.
A wide range of Platforms and Languages: MySql is available for all major platforms like Linux, Windows, Mac, BSD, and Solaris. It also has connectors to languages like Node.js, Ruby, C#, C++, C, Java, Perl, PHP, and Python.
Cost-effectiveness: It is open source and free.
2. MS-SQL Server Express Edition
It is a powerful and user-friendly database which has excellent stability, reliability, and scalability with support from Microsoft. The following are some of MS-SQL benefits and strengths:
Integrated Development Environment: Microsoft visual studio, SQL Server Management Studio, and Visual Developer tools provide a beneficial way for development and increase the developer's productivity.
Disaster Recovery: It has good disaster recovery mechanism including database mirroring, failover clustering and RAID partitioning.
Cloud back-up: Microsoft also provides cloud storage when you perform a cloud-backup of your database
3. Oracle Express Edition
It is a limited edition of Oracle Enterprise Edition server with certain limitations. This database is free for development and deployment. The following are some of Oracle benefits and strengths:
Easy to Upgrade: Can be easily upgraded to the newer version, or an enterprise edition.
Wide platform support: It supports a wide range of platforms including Linux and Windows
Scalability: Although the scalability of this database does not cost useful as MySQL server, the solution is very reliable, secure, easily manageable and productive.
NoSQL Database Examples
1. MongoDB
MongoDB is one of the most famous documents based NoSQL database as it stores data in JSON like documents. It is a non-relational database with the dynamic schema. It has been developed by the founders of DoubleClick, written in C++ and is currently being used by some big companies like The New York Times, Craigslist, MTV Networks. The following are some of MongoDB benefits and strengths:
Speed: For simple queries, it gives a good performance, as all the related data are in a single document which eliminates the join operations.
Scalability: It is horizontally scalable, i.e., you can reduce the workload by increasing the number of servers in your resource pool instead of relying on a stand-alone resource.
Manageable: It is easy to use for both developers and administrators. This also gives the ability to shard database
Dynamic Schema: It gives you the flexibility to evolve your data schema without modifying the existing data
2. CouchDB
CouchDB is also a document based NoSQL database. It stores data in the form of JSON documents. The following are some of CouchDB benefits and strengths:
Schema-less: As a member of the NoSQL family, it also has a dynamic schema which makes it more flexible, having a form of JSON documents for storing data.
HTTP query: You can access your database documents using your web browser.
Conflict Resolution: It has automatic conflict detection which is useful while in a distributed database.
Easy Replication: Implementing replication is relatively straightforward
3. Redis
Redis is another Open Source NoSQL database which is mainly used because of its lightning speed. It is written in ANSI C language. The following are some of Redis benefits and strengths:
Data structures: Redis provides efficient data structures to the extent that it is sometimes called a data structure server. The keys stored in a database can be hashes, lists, strings, sorted or unsorted sets.
Redis as Cache: You can use Redis as a cache by implementing keys with limited time to live to improve the performance.
Very fast: It is considered as one of the fastest NoSQL servers as it works with the in-memory dataset.




No comments:
Post a Comment